SLVSB17D March 2012 – April 2016 DRV8836
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- DSS|12
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DSS|12
発注情報
1 Features
- Dual-H-Bridge Motor Driver
- Capable of Driving Two DC Motors or One Stepper Motor
- Low MOSFET On-Resistance:
HS + LS 305 mΩ
- 1.5-A Maximum Drive Current Per H-Bridge
- Configure Bridges Parallel for 3-A Drive Current
- 2-V to 7-V Operating Supply Voltage
- Flexible PWM or PHASE/ENABLE Interface
- Low-Power Sleep Mode With 95-nA Maximum Supply Current
- Dedicated nSLEEP Input Pin
- Tiny 2.00-mm × 3.00-mm WSON Package
2 Applications
- Battery-Powered:
- DSLR Lenses
- Consumer Products
- Toys
- Robotics
- Cameras
- Medical Devices
3 Description
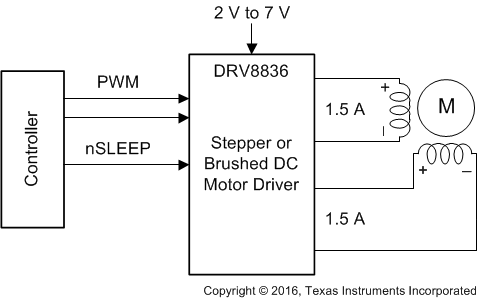
The DRV8836 provides an integrated motor driver solution for cameras, consumer products, toys, and other low-voltage or battery-powered motion control applications. The device has two H-bridge drivers, and can drive two DC motors or one stepper motor, as well as other devices like solenoids. The output driver block for each consists of N-channel power MOSFET configured as an H-bridge to drive the motor winding. An internal charge pump generates gate drive voltages.
The DRV8836 supplies up to 1.5-A of output current per H-bridge. It operates on a power supply voltage from 2 V to 7 V.
PHASE/ENABLE and IN/IN interfaces can be selected which are compatible with industry-standard devices. A low-power sleep mode is provided which turns off all unnecessary logic to provide a very low current state.
Internal shutdown functions are provided for overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, undervoltage lockout, and overtemperature.
The DRV8836 is packaged in a tiny 12-pin WSON package (Eco-friendly: RoHS and no Sb/Br).
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| DRV8836 | WSON (12) | 2.00 mm x 3.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the datasheet.