SLVS888C December 2008 – October 2015 TPS60150
PRODUCTION DATA.
1 Features
- 2.7-V to 5.5-V Input Voltage Range
- Fixed Output Voltage of 5 V
- Maximum Output Current: 140 mA
- 1.5-MHz Switching Frequency
- Typical 90-μA Quiescent Current at No Load Condition (Skip Mode)
- X2 Charge Pump
- Hardware Enable and Disable Function
- Built-in Soft Start
- Built-in Undervoltage Lockout Protection
- Thermal and Overcurrent Protection
- Available in a 2-mm × 2-mm 6-Pin SON Package with 0.8-mm Height
2 Applications
- USB On-the-Go (OTG)
- HDMI
- Portable Communication Devices
- PCMCIA Cards
- Mobile Phones, Smart Phones
- Handheld Meters
3 Description
The TPS60150 device is a switched capacitor voltage converter that produces a regulated, low noise, and low-ripple output voltage of 5 V from an unregulated input voltage.
The 5-V output can supply a minimum of 140-mA current.
The TPS60150 device operates in skip mode when the load current falls less than 8 mA under typical condition. In skip mode operation, quiescent current is reduced to 90 μA.
Only 3 external capacitors are needed to generate the output voltage, therefore saving PCB space.
Inrush current is limited by the soft-start function during power on and power transient states.
The TPS60150 device operates over a free-air temperature range of –40°C to 85°C. The device is available with a small 2-mm × 2-mm 6-pin SON package (QFN).
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS60150 | WSON (6) | 2.00 mm × 2.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
space
space
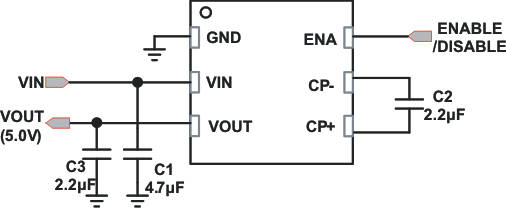
Typical Application Schematic
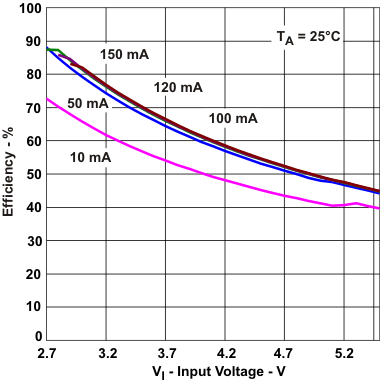
Efficiency vs Input Voltage