-
INA20x オープン・ドレイン・コンパレータおよび基準電圧搭載のハイサイド測定、電流シャント・モニタ
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
- 重要なお知らせ
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
INA20x オープン・ドレイン・コンパレータおよび基準電圧搭載のハイサイド測定、電流シャント・モニタ
1 特長
- 完全な電流検出ソリューション
- 3つのゲイン・オプションを利用可能:
- INA200: 20V/V
- INA201: 50V/V
- INA202: 100V/V
- 0.6Vの内部基準電圧
- 内蔵のオープン・ドレイン・コンパレータ
- コンパレータのラッチ機能
- 同相範囲: -16V~80V
- 高精度: 温度範囲にわたって最大誤差3.5%
- 帯域幅: 500kHz (INA200)
- 静止電流: 1800μA (最大値)
- パッケージ: SOIC-8、VSSOP-8
2 アプリケーション
- ノートブック・コンピュータ
- 携帯電話
- 通信機器
- オートモーティブ(車載)
- パワー・マネージメント
- バッテリ充電器
- 溶接機器
3 概要
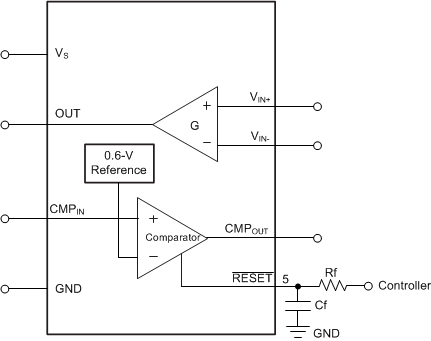
INA200、INA201、INA202デバイスは、ハイサイドの電圧出力、電流シャント・モニタで、コンパレータが内蔵されています。INA20xデバイスは、-16V~80Vの範囲の同相電圧において、シャントの両端の電圧降下を検出できます。INA20xシリーズは20V/V、50V/V、100V/Vの3つの出力電圧スケールで、500kHzまでの帯域幅で利用可能です。
INA200、INA201、INA202デバイスにはオープン・ドレインのコンパレータと、0.6Vのスレッショルドを提供する内部基準電圧が組み込まれています。外部の分圧抵抗により、電流トリップ点を設定します。コンパレータにはラッチ機能があり、RESETピンをグランドに接続(またはオープンに保持)することで透過的にできます。
INA200、INA201、INA202デバイスは2.7V~18Vの単一電源で動作し、消費電流は最大1800μAです。パッケージは、超小型のVSSOP-8とSOIC-8を選択できます。
すべてのバージョンは、拡張動作温度範囲の-40℃~+125℃で動作が規定されています。
製品情報(1)
| 型番 | パッケージ | 本体サイズ(公称) |
|---|---|---|
| INA200 INA201 INA202 |
SOIC (8) | 4.90mm×3.91mm |
| VSSOP (8) | 3.00mm×3.00mm |
- 提供されているすべてのパッケージについては、データシートの末尾にある注文情報を参照してください。
概略回路図
4 改訂履歴
Changes from D Revision (October 2015) to E Revision
- Reformatted Thermal Information table note Go
- Corrected typo in Voltage Output section in Electrical Characteristics tableGo
- Added text to Comparator subsection in Feature Description sectionGo
- Added Figure 31 to Feature Description sectionGo
- Added Output vs Supply Ramp Considerations subsection in Feature Description sectionGo
- Added Figure 36, Figure 37, and Figure 38Go
Changes from C Revision (October 2010) to D Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Thermal Information table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
Changes from B Revision (October, 2007) to C Revision
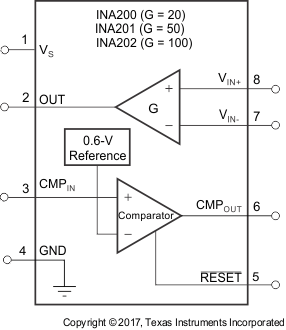
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
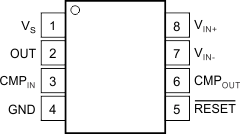
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CMPIN | 3 | Analog input | Comparator input |
| CMPOUT | 6 | Analog output | Comparator output |
| GND | 4 | Analog | Ground |
| OUT | 2 | Analog output | Output voltage |
| RESET | 5 | Analog input | Comparator reset pin, active low |
| VIN– | 7 | Analog input | Connect to shunt low side |
| VIN+ | 8 | Analog input | Connect to shunt high side |
| VS | 1 | Analog | Power supply |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, Vs | 2.7 | 18 | V | |
| Current-shunt monitor analog inputs, VIN+, VIN– | Differential (VIN+) – (VIN–) | –18 | 18 | V |
| Common-mode(2) | –16 | 80 | V | |
| Comparator analog input and reset pins(2) | GND – 0.3 | (Vs) + 0.3 | V | |
| Analog output, OUT(2) | GND – 0.3 | (Vs) + 0.3 | V | |
| Comparator output, OUT(2) | GND – 0.3 | 18 | V | |
| Input current into any pin(2) | 5 | mA | ||
| Operating temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Junction temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | ±4000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±1000 | ||||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCM | Common-mode input voltage | –16 | 12 | 80 | V |
| VS | Operating supply voltage | 2.7 | 12 | 18 | V |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 25 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | INA20x | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DGK (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 110.5 | 162.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 50.4 | 37.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 52.7 | 82.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.8 | 1.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 51.9 | 81.4 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Current-Shunt Monitor
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, and CMPIN = GND, (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | ||||||||
| VSENSE | Full-scale sense input voltage | VSENSE = VIN+ – VIN– | 0.15 | (VS – 0.25) / Gain | V | |||
| VCM | Common-mode input range | TA = –40°C to 125°C | –16 | 80 | V | |||
| CMR | Common-mode rejection | VIN+ = –16 V to 80 V | 80 | 100 | dB | |||
| VIN+ = 12 V to 80 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 100 | 123 | dB | |||||
| VOS | Offset voltage, RTI(1) | TA = 25°C | ±0.5 | ±2.5 | mV | |||
| TA = 25°C to 125°C | ±3 | mV | ||||||
| TA = –40°C to 25°C | ±3.5 | mV | ||||||
| dVOS/dT | Offset voltage, RTI, vs temperature | TMIN to TMAX, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 5 | μV/°C | ||||
| PSR | Offset voltage, RTI, vs power supply | VOUT = 2 V, VIN+ = 18 V, 2.7 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 2.5 | 100 | μV/V | |||
| IB | Input bias current, VIN– pin | TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±9 | ±16 | μA | |||
| OUTPUT (VSENSE ≥ 20 mV) | ||||||||
| G | Gain | INA200 | 20 | V/V | ||||
| INA201 | 50 | V/V | ||||||
| INA202 | 100 | V/V | ||||||
| Gain error | VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV | ±0.2% | ±1% | |||||
| VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV, TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±2% | |||||||
| Total output error(2) | VSENSE = 120 mV, VS = 16 V | ±0.75% | ±2.2% | |||||
| VSENSE = 120 mV, VS = 16 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±3.5% | |||||||
| Nonlinearity error(3) | VSENSE = 20 mV to 100 mV | ±0.002% | ||||||
| RO | Output impedance | 1.5 | Ω | |||||
| Maximum capacitive load | No sustained oscillation | 10 | nF | |||||
| OUTPUT (VSENSE < 20 mV)(4) | ||||||||
| Output | INA200, INA201, INA202 | –16 V ≤ VCM < 0 V | 300 | mV | ||||
| INA200 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 0.4 | V | |||||
| INA201 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 1 | V | |||||
| INA202 | 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS, VS = 5 V | 2 | V | |||||
| INA200, INA201, INA202 | VS < VCM ≤ 80 V | 300 | mV | |||||
| VOLTAGE OUTPUT(5) | ||||||||
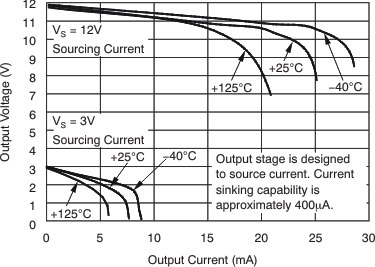
| Output swing to the positive rail | VIN– = 11 V, VIN+ = 12 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | (Vs) – 0.15 | (Vs) – 0.25 | V | ||||
| Output swing to GND(6) | VIN– = 0 V, VIN+ = –0.5 V, TA = –40°C to 125°C | (GND) + 0.004 | (GND) + 0.05 | V | ||||
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | ||||||||
| BW | Bandwidth | INA200 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 500 | kHz | |||
| INA201 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 300 | kHz | |||||
| INA202 | CLOAD = 5 pF | 200 | kHz | |||||
| Phase margin | CLOAD < 10 nF | 40 | °C | |||||
| SR | Slew rate | 1 | V/μs | |||||
| Settling time (1%) | VSENSE = 10 mVPP to 100 mVPP, CLOAD = 5 pF |
2 | μs | |||||
| NOISE, RTI | ||||||||
| Voltage noise density | 40 | nV/√Hz | ||||||
6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Comparator
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, and RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFFSET VOLTAGE | |||||||
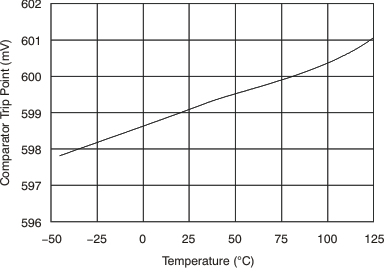
| Threshold | TA = 25°C | 590 | 608 | 620 | mV | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 586 | 625 | mV | ||||
| Hysteresis(1) | TA = –40°C to 85°C | –8 | mV | ||||
| INPUT BIAS CURRENT(2) | |||||||
| Input bias current, CMPin PIN | 0.005 | 10 | nA | ||||
| Input bias current, CMPin PIN, vs temperature | TA = –40°C to 125°C | 15 | nA | ||||
| INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE | |||||||
| Input voltage range, CMPin PIN | 0 V to VS – 1.5 V | V | |||||
| OUTPUT (OPEN-DRAIN) | |||||||
| Large-signal differential voltage gain | CMP VOUT 1 V to 4 V, RL ≥ 15 kΩ connected to 5 V |
200 | V/mV | ||||
| ILKG | High-level leakage current(3)(4) | VID = 0.4 V, VOH = VS | 0.0001 | 1 | μA | ||
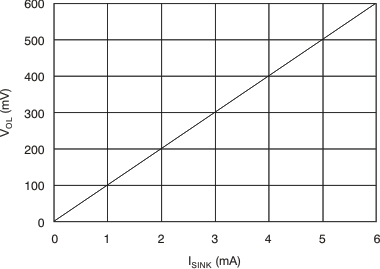
| VOL | Low-level output voltage(3) | VID = –0.6 V, IOL = 2.35 mA | 220 | 300 | mV | ||
| RESPONSE TIME | |||||||
| Response time(5) | RL to 5 V, CL = 15 pF, 100-mV Input Step with 5-mV overdrive | 1.3 | μs | ||||
| RESET | |||||||
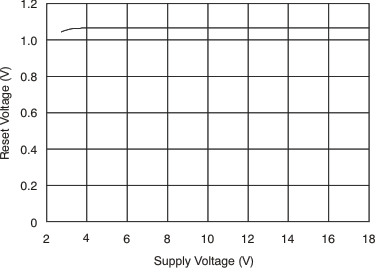
| RESET threshold(6) | 1.1 | V | |||||
| Logic input impedance | 2 | MΩ | |||||
| Minimum RESET pulse width | 1.5 | μs | |||||
| RESET propagation delay | 3 | μs | |||||
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: General
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VCM = 12 V, VSENSE = 100 mV, RL = 10 kΩ to GND, RPULL-UP = 5.1 kΩ connected from CMPOUT to VS, and CMPIN = 1 V, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER SUPPLY | |||||||
| VS | Operating power supply | TA = –40°C to 125°C | 2.7 | 18 | V | ||
| IQ | Quiescent current | VOUT = 2 V | 1350 | 1800 | μA | ||
| VSENSE = 0 mV, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1850 | μA | |||||
| Comparator power-on reset threshold(1) | 1.5 | V | |||||
| TEMPERATURE | |||||||
| Specified temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||||
| Operating temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | ||||
| Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | ||||
| θJA | Thermal resistance | VSSOP-8 Surface-Mount | 200 | °C/W | |||
| SOIC-8 | 150 | °C/W | |||||
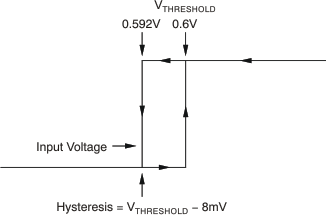 Figure 1. Typical Comparator Hysteresis
Figure 1. Typical Comparator Hysteresis
6.8 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = 12 V, VIN+ = 12 V, and VSENSE = 100 mV, (unless otherwise noted)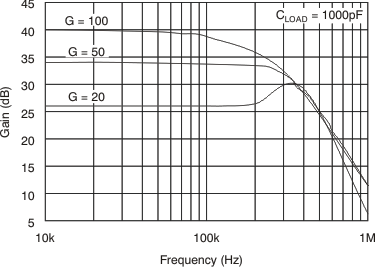
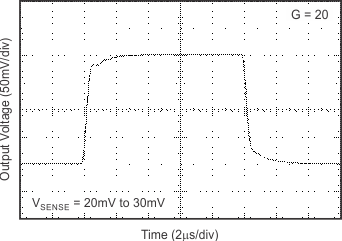
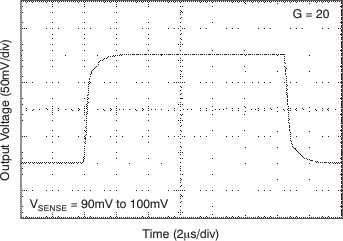
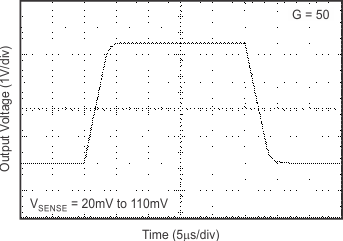
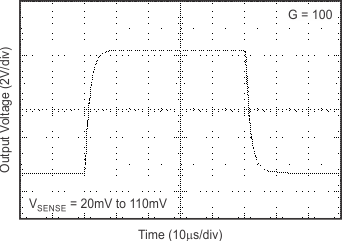
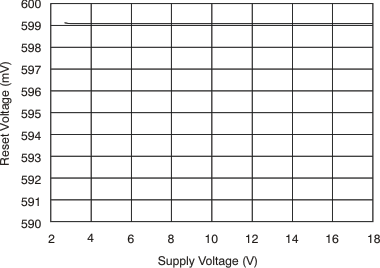
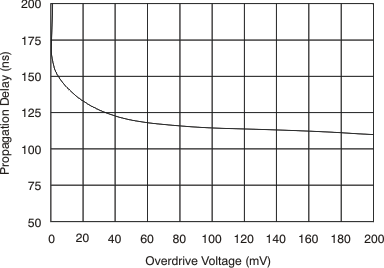
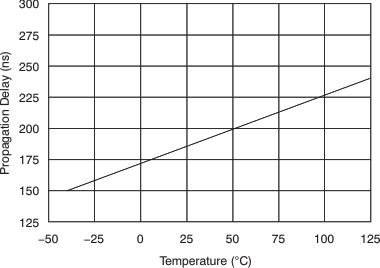
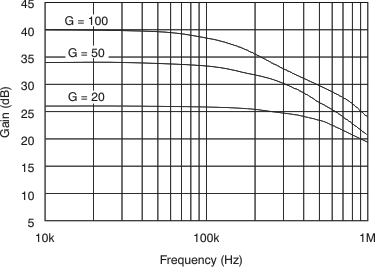
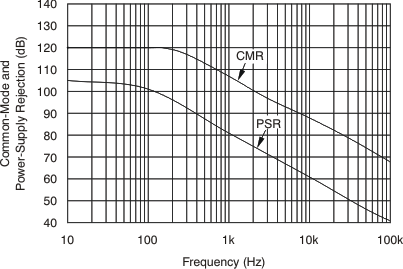
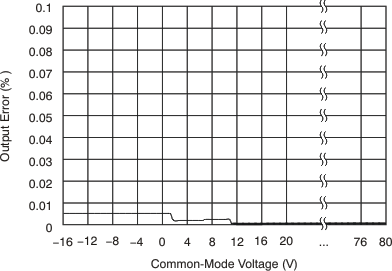
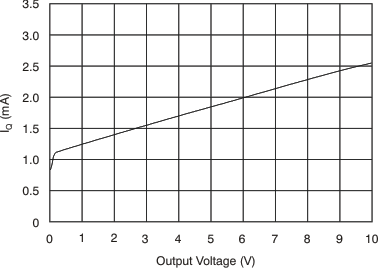
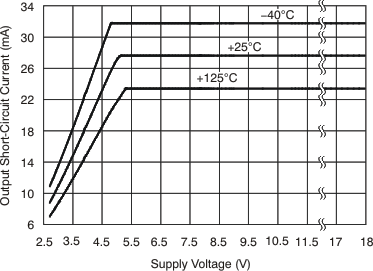
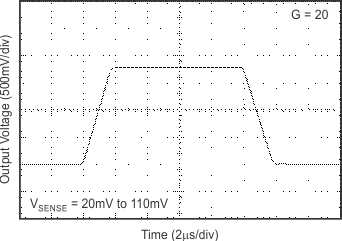
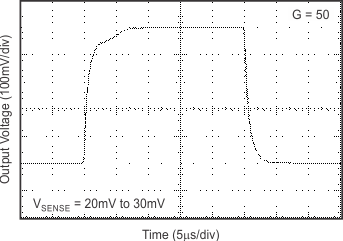
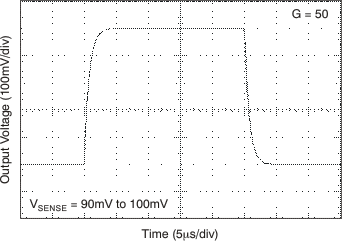
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The INA200, INA201, and INA202 devices are high-side current-shunt monitors with voltage output. The INA20x devices can sense drops across shunts at common-mode voltages from –16 V to 80 V. The INA200–INA202 devices are available with three output voltage scales: 20 V/V, 50 V/V, and 100 V/V, with up to 500-kHz bandwidth. The INA200, INA201, and INA202 devices incorporate an open-drain comparator and internal reference providing a 0.6-V threshold. External dividers set the current trip point. The comparator includes a latching capability, that can be made transparent by grounding (or leaving open) the RESET pin. The INA200, INA201, and INA202 devices operate from a single 2.7 to 18-V supply, drawing a maximum of 1800 μA of supply current. Package options include the very small MSOP-8 and the SO-8. All versions are specified over the extended operating temperature range of –40°C to +125°C.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
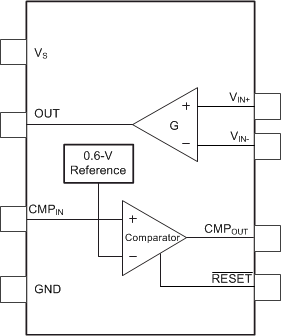
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Basic Connections
Figure 26 shows the basic connections of the INA20x devices. The input pins (VIN+ and VIN–) must be connected as closely as possible with Kelvin connections to the shunt resistor to minimize any resistance in series with the shunt resistance.
Power-supply bypass capacitors are required for stability. Applications with noisy or high-impedance power supplies may require additional decoupling capacitors to reject power-supply noise. Connect bypass capacitors close to the device pins.
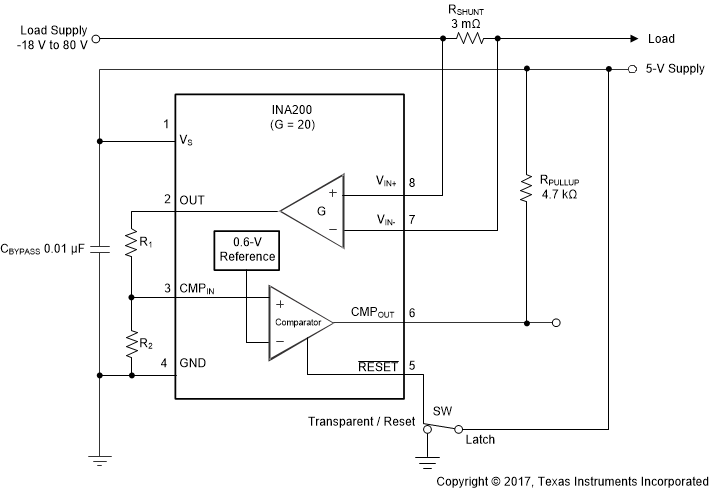 Figure 26. INA200 Basic Connections
Figure 26. INA200 Basic Connections
7.3.2 Selecting RS
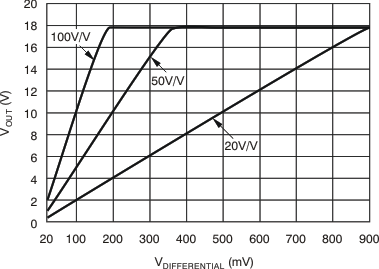
The selected value for the shunt resistor, RS, depends on the application and is a compromise between small-signal accuracy and maximum permissible voltage loss in the measurement line. High values of RS provide better accuracy at lower currents by minimizing the effects of offset, while low values of RS minimize voltage loss in the supply line. For most applications, using an RS value that provides a full-scale shunt voltage range of 50 mV to 100 mV results in the best performance. Maximum input voltage for accurate measurements is 500 mV, but output voltage is limited by supply.
7.3.3 Comparator
The INA200, INA201, and INA202 devices incorporate an open-drain comparator. This comparator typically has 2 mV of offset and a 1.3-μs (typical) response time. The output of the comparator latches and is reset through the RESET pin; see Figure 28.
When Vs and RESET are different, TI recommends adding a low-pass filter (LPF) on the RESET pin to avoid comparator behavior inconsistent with the data sheet. For instance, with a 12-V supply and a 3.3-V RESET, a rise time of 400 ns is appropriate. Similarly, with an 18-V supply and a 2.7-V RESET, a 1-µs rise time is appropriate; see Figure 31.
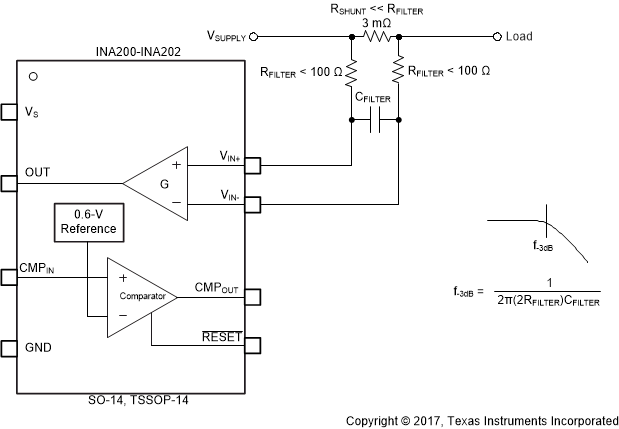 Figure 27. Input Filter (Gain Error: 1.5% to 2.8%)
Figure 27. Input Filter (Gain Error: 1.5% to 2.8%)
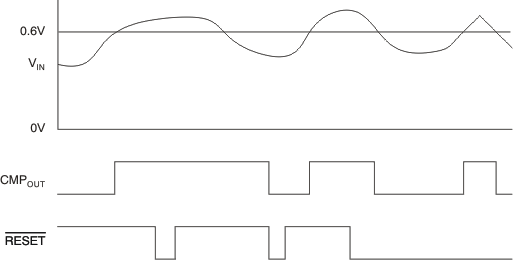 Figure 28. Comparator Latching Capability
Figure 28. Comparator Latching Capability
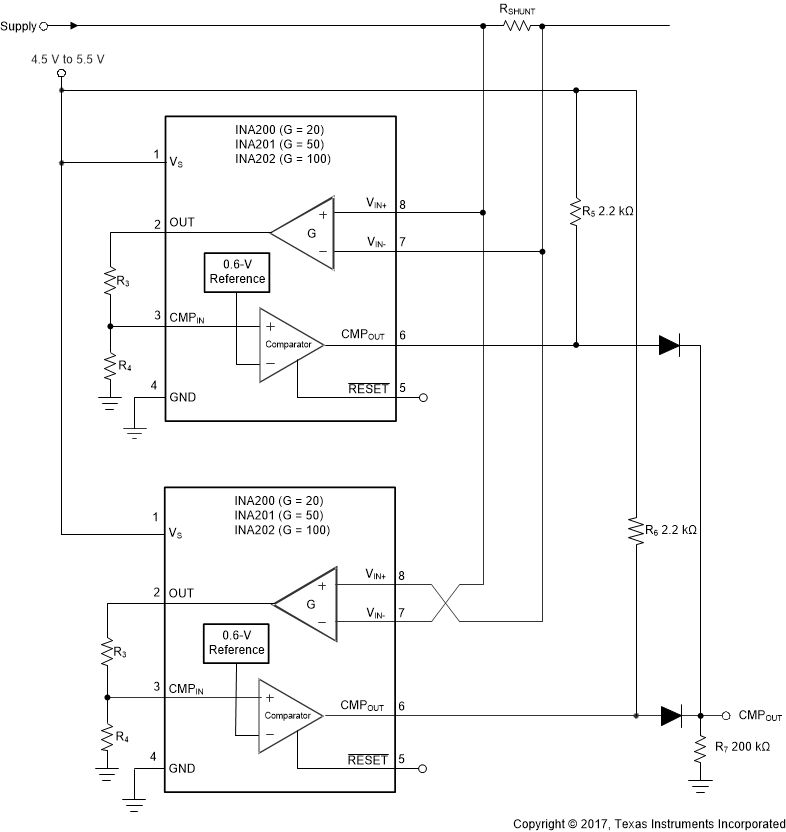
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Input Filtering
An obvious and straightforward location for filtering is at the output of the INA20x series; however, this location negates the advantage of the low output impedance of the internal buffer. The only other option for filtering is at the input pins of the INA20x devices, which is complicated by the internal 5 kΩ + 30% input impedance. This is shown in Figure 27. Using the lowest possible resistor values minimizes the initial shift in gain and effects of tolerance. The effect on initial gain is shown in Equation 1:
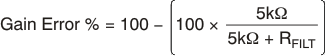
Total effect on gain error can be calculated by replacing the 5-kΩ term with 5 kΩ – 30%, (or 3.5 kΩ) or 5 kΩ + 30% (or 6.5 kΩ). The tolerance extremes of RFILT can be inserted into the equation. If a pair of 100-Ω 1% resistors are used on the inputs, the initial gain error equals 1.96%. Worst-case tolerance conditions always occur at the lower excursion of the internal 5-kΩ resistor (3.5 kΩ), and the higher excursion of RFILT – 3% in this case.
The specified accuracy of the INA20x devices must then be combined in addition to these tolerances. While this discussion treated accuracy worst-case conditions by combining the extremes of the resistor values, it is appropriate to use geometric mean or root sum square calculations to total the effects of accuracy variations.
7.4.2 Accuracy Variations as a Result of VSENSE and Common-Mode Voltage
The accuracy of the INA200, INA201, and INA202 current shunt monitors is a function of two main variables: VSENSE (VIN+ – VIN–), common-mode voltage, (VCM), relative to the supply voltage (VS). VCM is expressed as (VIN+ + VIN–) / 2; however, in practice, VCM is seen as the voltage at VIN+ because the voltage drop across VSENSE is typically small.
This section addresses the accuracy of these specific operating regions:
- Normal Case 1: VSENSE ≥ 20 mV, VCM ≥ VS
- Normal Case 2: VSENSE ≥ 20 mV, VCM < VS
- Low VSENSE Case 1: VSENSE < 20 mV, –16 V ≤ VCM < 0
- Low VSENSE Case 2: VSENSE < 20 mV, 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS
- Low VSENSE Case 3: VSENSE < 20 mV, VS < VCM ≤ 80 V
7.4.2.1 Normal Case 1: VSENSE ≥ 20 mv, VCM ≥ VS
This region of operation provides the highest accuracy. Here, the input offset voltage is characterized and measured using a two-step method. First, the gain is determined by Equation 2.
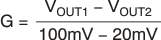
where
- VOUT1 = output voltage with VSENSE = 100 mV
- VOUT2 = output voltage with VSENSE = 20 mV
Then the offset voltage is measured at VSENSE = 100 mV, and referred to the input (RTI) of the current shunt monitor, as shown in Electrical Characteristics: Current-Shunt Monitor.
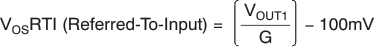
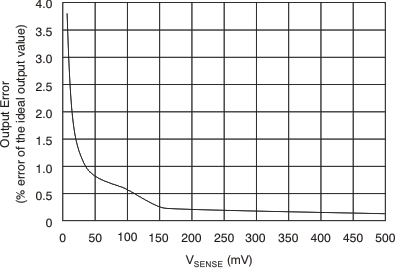
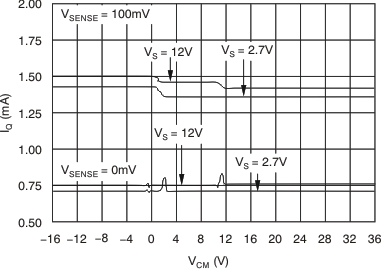
In the Typical Characteristics, Figure 7 shows the highest accuracy for the this region of operation. In this plot, VS = 12 V. For VCM ≥ 12 V, the output error is at the minimum value. This case creates the VSENSE ≥ 20-mV output specifications in Electrical Characteristics: Current-Shunt Monitor .
7.4.2.2 Normal Case 2: VSENSE ≥ 20 mv, VCM < VS
This region of operation is less accurate than normal case 1 as a result of the common-mode operating area in which the part functions, as shown in the Figure 7 curve (Figure 7). As noted, for this graph VS = 12 V; for VCM < 12 V, the output error increases as VCM decreases to less than 12 V, with a typical maximum error of 0.005% at the most negative VCM = –16 V.
7.4.2.3 Low VSENSE Case 1: VSENSE < 20 mV, –16 V ≤ VCM < 0
and Low VSENSE Case 3: VSENSE < 20 mV, VS < VCM ≤ 80 V
Although the INA200 family of devices are not designed for accurate operation in these regions, some applications are exposed to these conditions. For example, when monitoring power supplies that are switched on and off while VS is still applied to the INA20x devices, it is important to know what the behavior of the devices is in these regions.
As VSENSE approaches 0 mV, in these VCM regions, the accuracy of the device output degrades. A larger-than-normal offset can appear at the current shunt monitor output with a typical maximum value of VOUT = 300 mV for
VSENSE = 0 mV. As VSENSE approaches 20 mV, VOUT returns to the expected output value with accuracy as shown in Electrical Characteristics: Current-Shunt Monitor. Figure 32 shows this effect using the INA202 (gain = 100).
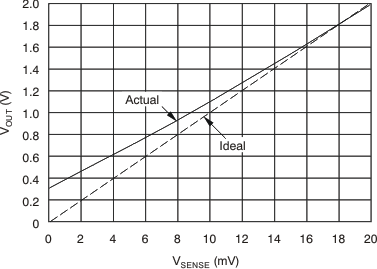 Figure 32. Example For Low VSENSE Cases 1 and 3 (INA202, Gain = 100)
Figure 32. Example For Low VSENSE Cases 1 and 3 (INA202, Gain = 100)
7.4.2.4 Low VSENSE Case 2: VSENSE < 20 mV, 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ VS
This region of operation is the least accurate for the INA20x family. To achieve the wide input common-mode voltage range, these devices use two op amp front ends in parallel. One op amp front end operates in the positive input common-mode voltage range, and the other in the negative input region. For this case, neither of these two internal amplifiers dominates and overall loop gain is low. Within this region, VOUT approaches voltages close to linear operation levels for normal case 2. This deviation from linear operation becomes greatest the closer VSENSE approaches 0 V. Within this region, as VSENSE approaches 20 mV, device operation is closer to that is described in normal case 2. Figure 33 shows this behavior for the INA202. The VOUT maximum peak for this case is tested by maintaining a constant VS, setting VSENSE equal to 0 mV and sweeping VCM from 0 V to VS. The exact VCM at which VOUT peaks during this test varies from device to device, but the VOUT maximum peak is tested to be less than the specified VOUT tested limit.
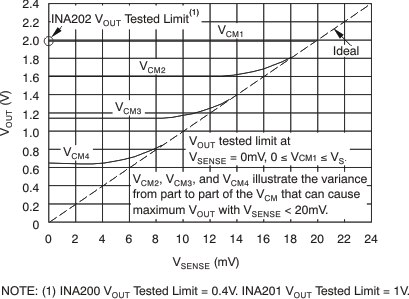 Figure 33. Example For Low VSENSE Case 2 (INA202, Gain = 100)
Figure 33. Example For Low VSENSE Case 2 (INA202, Gain = 100)
7.4.3 Transient Protection
The –16 to 80 V common-mode range of the INA20x devices is ideal for withstanding automotive fault conditions ranging from 12-V battery reversal up to 80-V transients, since no additional protective components are required up to those levels. In the event that the INA20x devices are exposed to transients on the inputs in excess of their ratings, then external transient absorption with semiconductor transient absorbers (such as Zeners) are required. TI does not recommend using MOVs or VDRs, except when they are used in addition to a semiconductor transient absorber. Select the transient absorber so the absorber does not allow the INA20x devices to be exposed to transients greater than 80 V (that is, allow for transient absorber tolerance and additional voltage due to transient absorber dynamic impedance). Despite the use of internal Zener-type ESD protection, the INA20x devices do not lend themselves to using external resistors in series with the inputs since the internal gain resistors can vary up to ±30%. (If gain accuracy is not important, then resistors can be added in series with the INA200, INA201, and INA202 inputs with two equal resistors on each input.)
7.4.4 Output Voltage Range
The output of the INA20x devices is accurate within the output voltage swing range set by the power supply pin (VS.) This performance is best illustrated when using the INA202 (a gain of 100 version), where a 100-mV full-scale input from the shunt resistor requires an output voltage swing of 10 V, and a power-supply voltage sufficient to achieve 10 V on the output.
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
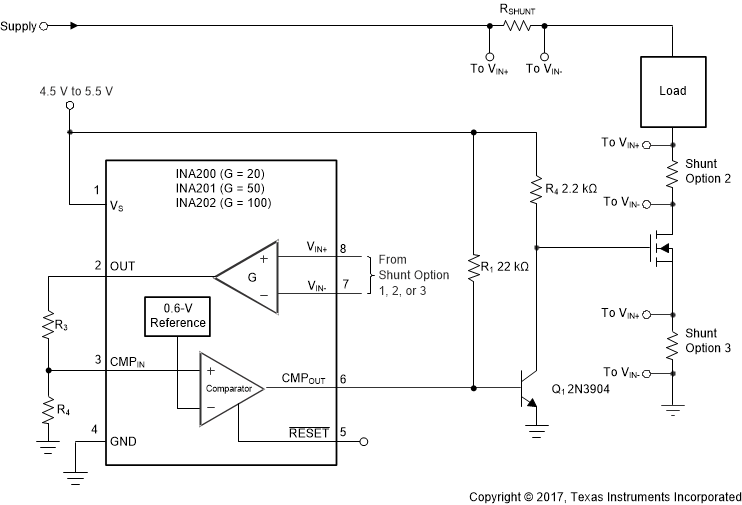
The INA20x series is designed to enable simple configuration for detecting overcurrent conditions and current monitoring in an application. This device is individually targeted towards overcurrent detection of a single threshold. However, this device can pair with additional devices and circuitry to create more complex monitoring functional blocks.
8.2 Typical Application
8.2.1 Design Requirements
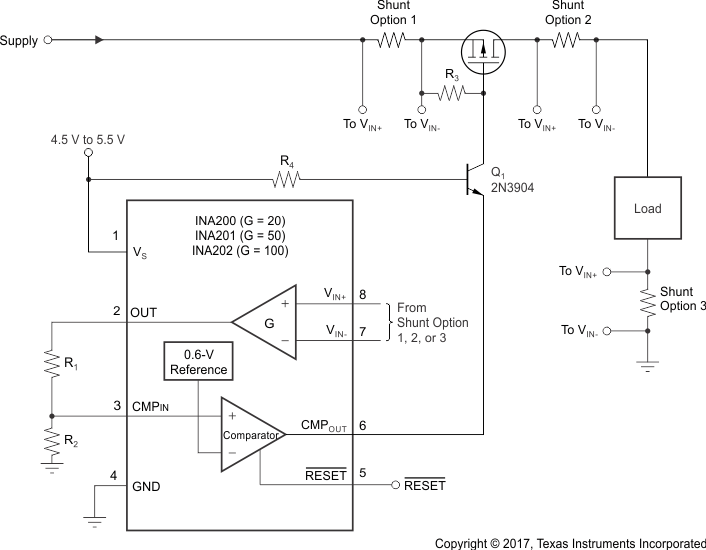
The device measures current through a resistive shunt with current flowing in one direction that enables detection of an overcurrent event only when the differential input voltage exceeds the threshold limit. When the current reaches the set limit of the divider R1 / R2, the output of CMPOUT transitions high, which turns Q1 on, pulls the gate of the pass-FET low, and turns off the flow off current.
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Figure 34 shows the basic connections of the device. The input terminals (IN+ and IN –) must be connected as closely as possible to the current-sensing resistor to minimize any resistance in series with the shunt resistance. Additional resistance between the current-sensing resistor and input terminals results in errors in the measurement. When input current flows through this external input resistance, the voltage developed across the shunt resistor differs from the voltage reaching the input terminals.
Use the gain of the INA20x and shunt value to calculate the OUT voltage for the desired trip current. Configure R1 and R2 so that the current trip point is equal to the 0.6-V reference voltage.
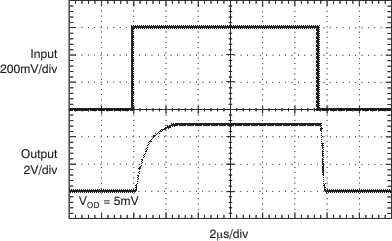
8.2.3 Application Curve
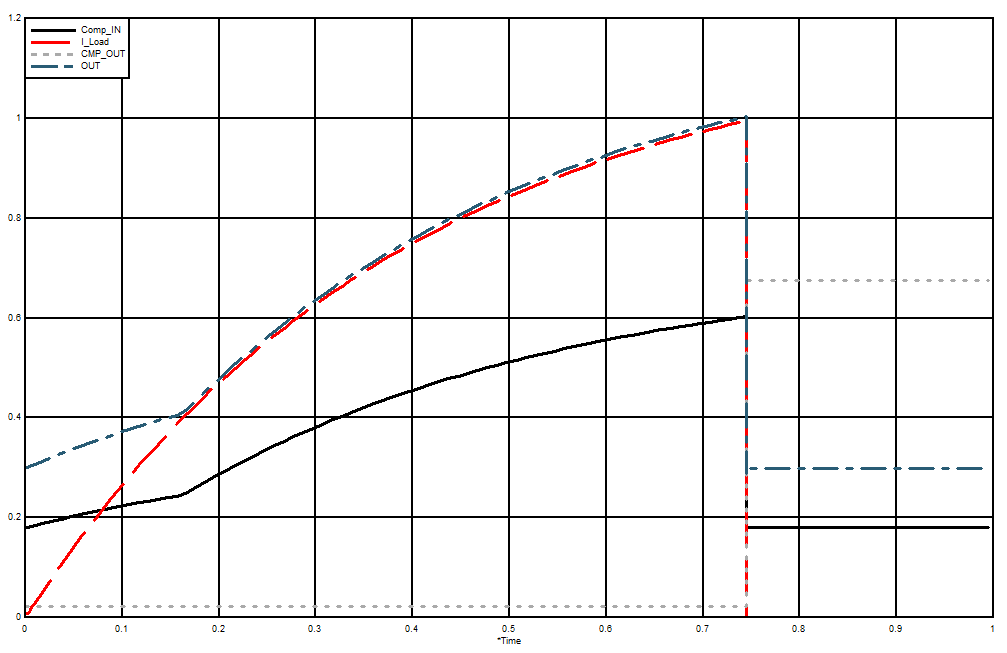 Figure 35. Low-Side Switch Overcurrent Shutdown Response
Figure 35. Low-Side Switch Overcurrent Shutdown Response