-
TPS7A39 Dual, 150-mA, Wide VIN Positive and Negative LDO Voltage Regulator
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Setting the Output Voltages on Adjustable Devices
- 8.1.2 Capacitor Recommendations
- 8.1.3 Input and Output Capacitor (CINx and COUTx)
- 8.1.4 Feed-Forward Capacitor (CFFx)
- 8.1.5 Noise-Reduction and Soft-Start Capacitor (CNR/SS)
- 8.1.6 Buffered Reference Voltage
- 8.1.7 Overriding Internal Reference
- 8.1.8 Start-Up
- 8.1.9 AC and Transient Performance
- 8.1.10 DC Performance
- 8.1.11 Reverse Current
- 8.1.12 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power-Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
TPS7A39 Dual, 150-mA, Wide VIN Positive and Negative LDO Voltage Regulator
1 Features
- Positive and Negative LDOs in One Package
- Wide Input Voltage Range: ±3.3 V to ±33 V
- Wide Output Voltage Range:
- Positive Range: 1.2 V to 30 V
- Negative Range: –30 V to 0 V
- Output Current: 150 mA per Channel
- Monotonic Start-Up Tracking
- High Power-Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR):
- 69 dB (120 Hz)
- ≥ 50 dB (10 Hz to 2 MHz)
- Output Voltage Noise: 21 µVRMS (10 Hz–100 kHz)
- Buffered 1.2-V Reference Output
- Stable With a 10-µF or Larger Output Capacitor
- Single Positive-Logic Enable
- Adjustable Soft-Start In-Rush Control
- 3-mm × 3-mm, 10-Pin WSON Package
- Low Thermal Resistance: RθJA = 44.4°C/W
- Operating Temperature Range: –40 to +125°C
2 Applications
- Supply Rails for Op Amps, ADCs, DACs, and Other High-Precision Analog Circuitry
- Post DC-DC Regulation and Filtering
- Analog I/O Modules
- Test and Measurement
- Rx, Tx, and PA Circuitry
- Industrial Instrumentation
- Medical Imaging
3 Description
The TPS7A39 device is a dual, monolithic, high-PSRR, positive and negative low-dropout (LDO) voltage regulator capable of sourcing (and sinking) up to 150 mA of current. The regulated outputs can be independently and externally adjusted to symmetrical or asymmetrical voltages, making this device an ideal dual, bipolar power supply for signal conditioning.
Both positive and negative outputs of the TPS7A39 ratiometrically track each other during startup to mitigate floating conditions and other power-supply sequencing issues common in dual-rail systems. The negative output can regulate up to 0 V, extending the common-mode range for single-supply amplifiers. The TPS7A39 also features high PSRR to eliminate power-supply noise, such as switching noise, that can compromise signal integrity.
Both regulators are controlled with a single positive logic enable pin for interfacing with standard digital logic. A capacitor-programmable soft-start function controls in-rush current and start-up time. The internal reference voltage of the TPS7A39 can be overridden with an external reference to enable precision outputs, output voltage margining, or to track other power supplies. Additionally, the TPS7A39 has a buffered reference output that can be used as a voltage reference for other components in the system.
These features make the TPS7A39 a robust, simplified solution to power operational amplifiers, digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and other precision analog circuitry.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS7A39 | WSON (10) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Powering the Signal Chain
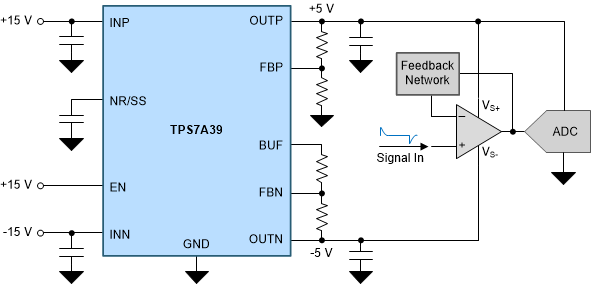
Monotonic Start-Up Tracking
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | INP | I | Positive input. A 10-μF(1) or larger capacitor must be tied from this pin to ground to ensure stability. Place the input capacitor as close to the input as possible; see the Capacitor Recommendations section for more information. |
| 2 | EN | I | Enable pin. Driving this pin to logic high (VEN ≥ VIH(EN)) enables the device; driving this pin to logic low (VEN ≤ VIL(EN)) disables the device. If enable functionality is not required, this pin must be connected to INP; see the Application and Implementation section for more detail. The enable voltage cannot exceed the input voltage (VEN ≤ VINP). |
| 3 | NR/SS | — | Noise-reduction, soft-start pin. Connecting an external capacitor between this pin and ground reduces reference voltage noise and enables soft-start and start-up tracking. A 10-nF or larger capacitor (CNR/SS) is recommended to be connected from NR/SS to GND to maximize or optimize ac performance and to ensure start-up tracking. This pin can also be driven externally to provide greater output voltage accuracy and lower noise, see the User-Settable Buffered Reference section for more information. |
| 4 | GND | — | Ground pin. This pin must be connected to ground and the thermal pad with a low-impedance connection. |
| 5 | INN | I | Negative input. A 10-μF(1) or larger capacitor must be tied from this pin to ground to ensure stability. Place the input capacitor as close to the input as possible; see the Capacitor Recommendations section for more information. |
| 6 | OUTN | O | Negative output. A 10-μF(1) or larger capacitor must be tied from this pin to ground to ensure stability. Place the output capacitor as close to the output as possible; see the Capacitor Recommendations section for more information. |
| 7 | FBN | I | Negative output feedback pin. This pin is used to set the negative output voltage. Although not required, a 10-nF feed-forward capacitor from FBN to OUTN (as close to the device as possible) is recommended to maximize ac performance. Nominally this pin is regulated to VFBN. Do not connect to ground. |
| 8 | BUF | O | Buffered reference output. This pin is connected to FBN through R2 and the voltage at this node is inverted and scaled up by the negative feedback network to provide the desired output voltage. The buffered reference can be used to drive external circuits, and has a 1-mA maximum load. |
| 9 | FBP | I | Positive output feedback pin. This pin is used to set the positive output voltage. Although not required, a 10-nF feed-forward capacitor from FBP to OUTP (as close to the device as possible) is recommended to maximize ac performance. Nominally this pin is regulated to VFBP. Do not connect this pin directly to ground. |
| 10 | OUTP | O | Positive output. A 10-μF(1) or larger capacitor must be tied from this pin to ground to ensure stability. Place the output capacitor as close to the output as possible; see the Capacitor Recommendations section for more information. |
| Pad | Thermal Pad | — | Connect the thermal pad to a large-area ground plane. The thermal pad is internally connected to GND. |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | INP | –0.3 | 36 | V |
| INN | –36 | 0.3 | ||
| OUTP | –0.3 | VINP + 0.3(5) | ||
| OUTN | VINN – 0.3(4) | 0.3 | ||
| FBP | –0.3 | VINP + 0.3(7) | ||
| BUF | –1 | VINP + 0.3(7) | ||
| NR/SS | –0.3 | VINP + 0.3(8) | ||
| FBN | VINN – 0.3(3) | 0.3 | ||
| EN | –0.3 | VINP + 0.3(6) | ||
| Current | Output current | Internally limited | ||
| Buffer current | 2 | mA | ||
| Temperature | Operating junction temperature, TJ | –55 | 150 | °C |
| Storage, Tstg | –65 | 150 | ||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |VINx| | Supply voltage magnitude for either regulator | 3.3 | 33 | V | |
| VEN | Enable supply voltage | 0 | VINP | V | |
| VOUTP | Positive regulated output voltage range | VFBP | 30 | V | |
| VOUTN | Negative regulated output voltage range | –30 | VFBN | V | |
| IOUTx | Output current for either regulator | 0.005(2) | 150 | mA | |
| IBUF | Output current from the BUF pin | 0 | 120 | 1000 | µA |
| CINx | Input capacitor for either regulator | 4.7 | 10(1) | µF | |
| COUTx | Output capacitor for either regulator | 4.7 | 10(1) | µF | |
| CNR/SS | Noise-reduction and soft-start capacitor | 0(3) | 10 | 1000 | nF |
| CFFP | Positive channel feed-forward capacitor; connect from VOUTP to FBP | 0 | 10 | 100 | nF |
| CFFN | Negative channel feed-forward capacitor; connect from VOUTN to FBN | 0 | 10 | 100 | nF |
| R2P | Lower positive feedback resistor | 10 | 240 | kΩ | |
| R2N | Lower negative feedback resistor (from FBN to BUF) | 10 | 240 | kΩ | |
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS7A39 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSC (WSON) | |||
| 10 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 44.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case(top) thermal resistance | 33.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 19.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 19.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case(bottom) thermal resistance | 2.9 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
at TJ = –40°C to +125°C, VINP(nom) = VOUTP(nom) + 1 V or VIN(nom) = 3.3 V (whichever is greater), VINN(nom) = VOUTN(nom) – 1 V or VINN(nom) = –3.3 V (whichever is less), VEN = VINP, IOUT = 1 mA, CINx = 2.2 μF, COUTx = 10 μF, CFFx = CNR/SS = open, R1N = R2N = 10 kΩ, and FBP tied to OUTP (unless otherwise noted); typical values are at TJ = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VINP | Input voltage range, positive channel | 3.3 | 33 | V | |||
| VINN | Input voltage range, negative channel | –33 | –3.3 | V | |||
| VUVLOP(rising) | Undervoltage lockout threshold, positive channel |
VINP rising, VINN = –3.3 V | 1.4 | 3.1 | V | ||
| VUVLOP(hys) | Undervoltage lockout threshold, positive channel hysteresis | VINP falling, VINN = –3.3 V | 120 | mV | |||
| VUVLON(falling) | Undervoltage lockout threshold, negative channel |
VINN falling, VINP = 3.3 V | –3.1 | –1.4 | V | ||
| VUVLON(hys) | Undervoltage lockout threshold, negative channel, hysteresis | VINN rising, VINP = 3.3 V | 70 | mV | |||
| VNR/SS | Internal reference voltage | 1.172 | 1.19 | 1.208 | V | ||
| VFBP | Positive feedback voltage | 1.170 | 1.188 | 1.206 | V | ||
| VFBN | Negative feedback voltage | –10 | 3.7 | 10 | mV | ||
| VOUT | Output voltage range(2) | Positive channel | VFBP | 30 | V | ||
| Negative channel | –30 | VFBN(1) | |||||
| VOUTP accuracy | VINP(nom) ≤ VINP ≤ 33 V, 1 mA ≤ IOUTP ≤ 150 mA, 1.2 V ≤ VOUTP(nom) ≤ 30 V |
–1.5 | 1.5 | %VOUT | |||
| VOUTN accuracy(3) | –33 V ≤ VINN ≤ VINN(nom), –150 mA ≤ IOUTN ≤ –1 mA, –30 V ≤ VOUTN(nom) ≤ –1.2 V | –3 | 3 | %VOUT | |||
| Negative VOUT channel accuracy | –33 V ≤ VINN ≤ VINN(nom) , –150 mA ≤ IOUTN ≤ 1 mA, –1.2 V < VOUTN(nom) < 0 V | –36 | 36 | mV | |||
| –33 V ≤ VINN ≤ VINN(nom) , –150 mA ≤ IOUTN ≤ 1 mA, VOUTN(nom) = 0 V | –12 | 12 | |||||
| ΔVOUT(ΔVIN) / VOUT(NOM) | Line regulation, positive channel | VINP(nom) ≤ VINP ≤ 33 V | 0.035 | %VOUT | |||
| Line regulation, negative channel | –33 V ≤ VINN ≤ VOUT(nom) + 1 V | 0.125 | |||||
| ΔVOUT(ΔIOUT) / VOUT(NOM) | Load regulation, positive channel | 1 mA ≤ IOUTP ≤ 150 mA | –0.09 | %VOUT | |||
| Load regulation, negative channel | –150 mA ≤ IOUTN ≤ –1 mA | 0.715 | |||||
| VDO | Dropout voltage | Positive channel | IOUTP = 50 mA, 3.3 V ≤ VINP(nom) ≤ 33.0 V, VFBP = 1.070 V |
175 | 300 | mV | |
| IOUTP = 150 mA, 3.3 V ≤ VINP(nom) ≤ 33.0 V, VFBP = 1.070 V |
300 | 500 | |||||
| Negative channel | IOUTN = –50 mA, –3.3 V ≤ VINN(nom) ≤ –33.0 V, VFBN = 0.0695 V |
–250 | –145 | ||||
| IOUTN = –150 mA, –3.3 V ≤ VINN(nom) ≤ –33.0 V, VFBN = 0.0695 V |
–400 | –275 | |||||
| VBUF | Buffered reference output voltage | VNR/SS | V | ||||
| VBUF/IBUF | Buffered reference load regulation | IBUF = 100 µA to 1 mA | 1 | mV/mA | |||
| VBUF – VNR/SS | Output buffer offset voltage | VNR/SS = 0.25 V to 1.2 V | –4 | 3 | 8 | mV | |
| VOUTP–VOUTN | DC output voltage difference with a forced REF voltage | VNR/SS = 0.25 V to 1.2 V | –10 | 10 | %VNR/SS | ||
| ILIM | Current limit | Positive channel | VOUTP = 90% VOUTP(nom) | 200 | 330 | 500 | mA |
| Negative channel | VOUTN = 90% VOUTN(nom) | –500 | –300 | –200 | |||
| ISUPPLY | Supply current | Positive channel | IOUTP = 0 mA, R2N = open, VINP = 33 V | 75 | 150 | µA | |
| IOUTP = 150 mA, R2N = open, VINP = 33 V | 904 | ||||||
| Negative channel | IOUTN = 0 mA, VOUTN(nom)= 0 V, R2N = open, VINN = –33 V | –150 | –60 | ||||
| IOUTN = 150 mA, R2N = open, VINN = –33 V | –1053 | ||||||
| ISHDN | Shutdown supply current | Positive channel | VEN = 0.4 V, VINP = 33 V | 3.75 | 6.5 | µA | |
| Negative channel | VEN = 0.4 V, VINN = –33 V | –4.5 | –2.25 | ||||
| IFBx | Feedback pin leakage current | Positive channel | 5.5 | 100 | nA | ||
| Negative channel | –100 | –9.7 | |||||
| INR/SS | Soft-start charging current | VNR/SS = 0.9 V | 3 | 5.1 | 6.7 | µA | |
| IEN | Enable pin leakage current | VEN = VINP = 33 V | 0.02 | 1 | µA | ||
| VIH(EN) | Enable high-level voltage | 2.2 | VINP | V | |||
| VIL(EN) | Enable low-level voltage | 0 | 0.4 | V | |||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | |VIN| = 6 V, |VOUT(nom)| = 5 V, COUT = 10 μF, CNR/SS = CFF= 10 nF, f = 120 Hz | 69 | dB | |||
| Vn | Output noise voltage | Positive channel | VINP = 3.3 V, VOUTP(nom) = VNR/SS, COUTP = 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz | 20.63 | µVRMS | ||
| VINP = 6 V, VOUTP(nom) = 5 V, COUTP = 10 μF, CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz | 26.86 | ||||||
| Negative channel | VINN = –3 V, VOUTN(nom) = –VNR/SS, COUTP = 10 μF, CNR/SS = 10 nF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz | 22.13 | |||||
| VINN = –6 V, VOUTN(nom) = –5 V, COUTP = 10 μF, CNR/SS = CFF= 10 nF, BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz | 28.68 | ||||||
| RNR/SS | Filter resistor from band gap to NR pin | 350 | kΩ | ||||
| Tsd | Thermal shutdown temperature | Shutdown, temperature increasing | 175 | °C | |||
| Reset, temperature decreasing | 160 | ||||||
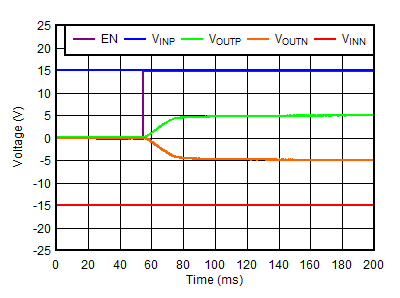
6.6 Startup Characteristics
at TJ = –40°C to +125°C, VINP(nom) = VOUTP(nom) + 1 V or VIN(nom) = 3.3 V (whichever is greater), VINN(nom) = VOUTN(nom) – 1 V or VINN(nom) = –3.3 V (whichever is less), VEN = VINP, IOUT = 1 mA, CINx = 2.2 μF, COUTx = 10 μF, CFFx = CNR/SS = 4.7nF, R1N = R2N = 10 kΩ, and FBP tied to OUTP (unless otherwise noted); typical values are at TJ = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tEN(delay) | Delay time from EN low-to-high transition to 2.5% VOUTP | From EN low-to-high transition to VOUTP = 2.5% × VOUTP(nom) | 300 | µs | ||
| tstart-up | Delay time from EN low-to-high transition to both outputs reaching 95% of final value | From EN low-to-high transition to VOUTP = VOUTP(nom) × 95% and VOUTN = VOUTN(nom) × 95% | 1.1 | ms | ||
| tPstart-Nstart | Delay time from VOUTP leaving a high-impedance state to VOUTN leaving a high-impedance state | From VOUTP = VOUTP(nom) × 2.5% to VOUTN = VOUTN(nom) × 2.5% | –40 | –17 | 40 | µs |
| Δ|VOUTP – VOUTN| | Voltage difference between the positive and negative output | During tPstart-Nstart | 75 | 300 | mV | |

NOTE:
Slow ramps (trise(VINx) > 10 ms typically) on VINx with EN tied to VINP does not meet the tracking specification. Use a resistor divider from VINP to EN for these applications.6.7 Typical Characteristics
at TJ = 25°C, VINP = VOUTP(nom) + 1.0 V or VIN = 3.3 V (whichever is greater), VINN = VOUTN(nom) – 1 V or –3.3 V (whichever is less), VEN = VIN, IOUT = 1 mA, CIN = 10-μF ceramic, COUT = 10-μF ceramic, and CFFP = CFFN = CNR/SS = 10 nF (unless otherwise noted)
| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 150 mA, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CFFx = 10 nF |


| IOUTP = 150 mA, VINP = VEN, VOUTN = –VOUTP, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, VINP = –VINN = 12 V |

| VINP = 5.5 V to 10 V at 1 V/µs, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, IOUTP = 150 mA |

| VINP = 5.5 V to 10 V at 4 V/µs, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, IOUTP = 150 mA |

| VINP = 6 V, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, IOUTP = 1 mA to 150 mA at 1 A/µs |

| VOUTN = 0 V |

| VOUTN = –1.19 V |

| VOUTN = –24 V |

| VOUTN = –15 V, VINN = –16 V |

| VOUTP = 1.188 V, VINP = 3.3 V |

| VOUTP = 30 V, VINP = 33 V |

| VOUTP = 15 V |

| VOUTP = 1.188 V |

Input Voltage

| VINP = 3.3 V |
Output Current


Output Voltage

| VOUTP = 1.188 V |

| VOUTN = –1.19 V |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = 150 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, VINN = –6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, VINN = –6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF, COUTP = 10 µF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, VINN = –6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, CNR/SS = CFFP = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = 5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, VINN = –6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, CFFx = 10 nF |


| IOUTN = –150 mA, VINP = VEN, VOUTN = –VOUTP, IOUTP = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = –150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = –150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, CNR/SS = 10 nF |

| VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTN = –150 mA, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTN = –5 V, VINP = VEN = 6 V, VOUTN = –5 V, IOUTP = 0 mA, CNR/SS = CFFx = 10 nF |

| VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, VINP = –VINN = 15 V |

| VINN = –5.5 V to –10 V at 1 V/µs, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = –150 mA, IOUTP = 0 mA |

| VINN = –5.5 V to –10 V at 4 V/µs, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = –150 mA, IOUTP = 0 mA |

| VINN = –6 V, VOUTP = –VOUTN = 5 V, IOUTN = 0 mA, IOUTN = –1 mA to –150 mA at 1 A/µs |

| VOUTN = 0 V, VINN = –3.3 V |

| VOUTN = –15 V |

| VOUTN = –1.2 V, VINN = –3.3 V |

| VOUTN = –30 V, VINN = –33 V |

| VOUTP = 15 V, VINP = 16 V |

| VOUTP = 1.188 V |

| VOUTP = 24 V |

| VOUTN = –1.19 V |

Input Voltage

| VOUTN = –3.3 V |
Output Current


Output Voltage

| VOUTN = –1.19 V |